Observability for Pipecat with Opik
Pipecat is an open-source Python framework for building real-time voice and multimodal conversational AI agents. Developed by Daily, it enables fully programmable AI voice agents and supports multimodal interactions, positioning itself as a flexible solution for developers looking to build conversational AI systems.
This guide explains how to integrate Opik with Pipecat for observability and tracing of real-time voice agents, enabling you to monitor, debug, and optimize your Pipecat agents in the Opik dashboard.
Account Setup
Comet provides a hosted version of the Opik platform, simply create an account and grab your API Key.
You can also run the Opik platform locally, see the installation guide for more information.
Getting started
To use the Pipecat integration with Opik, you will need to have Pipecat and the required OpenTelemetry packages installed:
Opik Cloud
Enterprise deployment
Self-hosted instance
Using Opik with Pipecat
For the basic example, you’ll need an OpenAI API key. You can set it as an environment variable:
Or set it programmatically:
Enable tracing in your Pipecat application by setting up OpenTelemetry instrumentation and configuring your pipeline task. For complete details on Pipecat’s OpenTelemetry implementation, see the official Pipecat OpenTelemetry documentation:
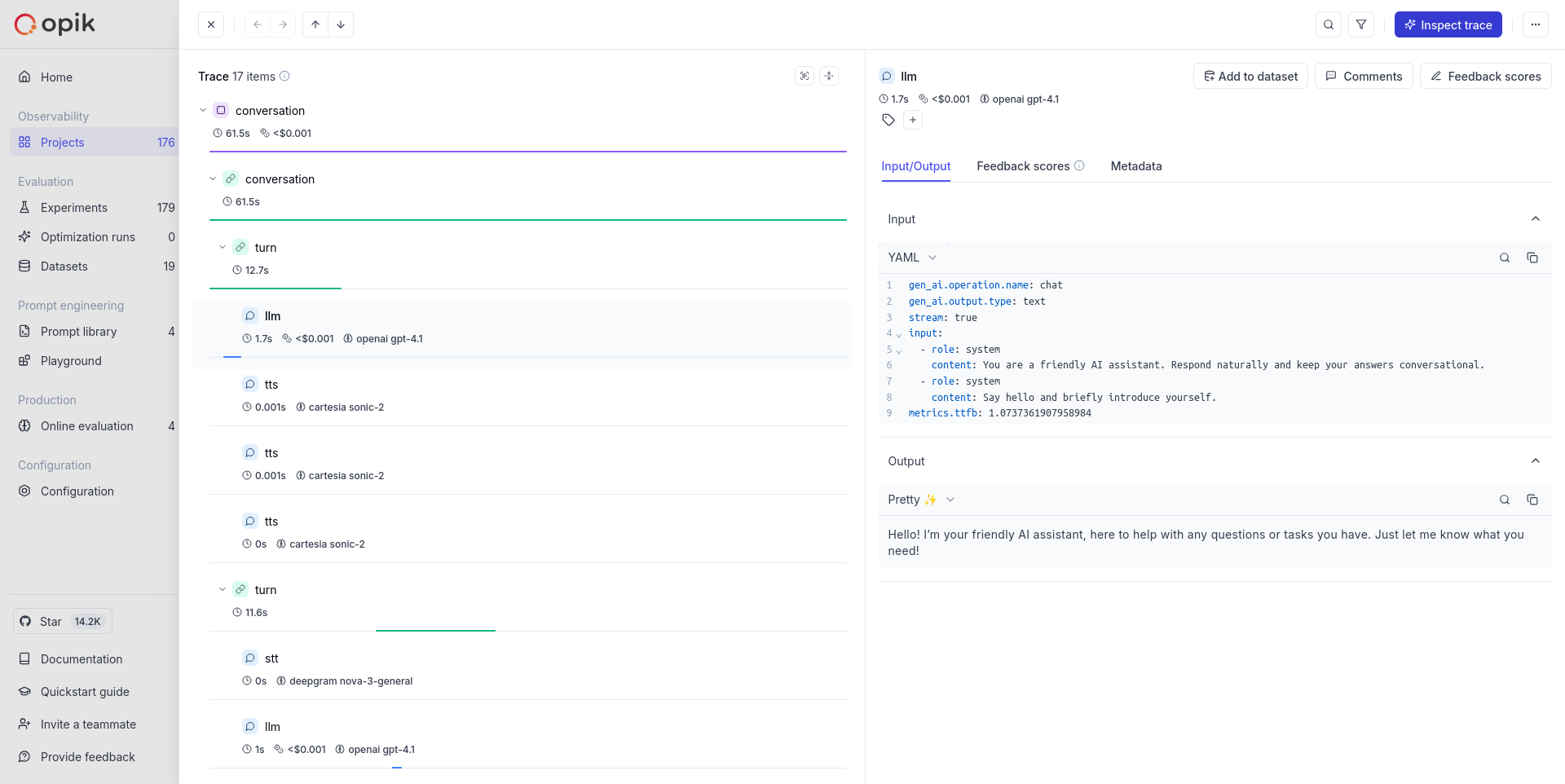
Trace Structure
Pipecat organizes traces hierarchically following the natural structure of conversations, as documented in their OpenTelemetry guide:
This structure allows you to track the complete lifecycle of conversations and measure latency for individual turns and services.
Understanding the Traces
Based on Pipecat’s OpenTelemetry implementation, the traces include:
- Conversation Spans: Top-level spans with conversation ID and type
- Turn Spans: Individual conversation turns with turn number, duration, and interruption status
- Service Spans: Detailed service operations with rich attributes:
- LLM Services: Model, input/output tokens, response text, tool configurations, TTFB metrics
- TTS Services: Voice ID, character count, synthesized text, TTFB metrics
- STT Services: Transcribed text, language detection, voice activity detection
- Performance Metrics: Time to first byte (TTFB) and processing durations for each service
Results viewing
Once your Pipecat applications are traced with Opik, you can view the OpenTelemetry traces in the Opik UI. You will see:
- Hierarchical conversation and turn structure as sent by Pipecat
- Service-level spans with the attributes Pipecat includes (LLM tokens, TTS character counts, STT transcripts)
- Performance metrics like processing durations and time-to-first-byte where provided by Pipecat
- Standard OpenTelemetry trace visualization and search capabilities
Getting Help
- Check the Pipecat OpenTelemetry Documentation for tracing setup and configuration
- Review the OpenTelemetry Python Documentation for general OTEL setup
- Visit the Pipecat GitHub repository for framework-specific issues
- Check Opik documentation for trace viewing and OpenTelemetry endpoint configuration
Further improvements
If you would like to see us improve this integration, simply open a new feature request on Github.

