Observability for OpenAI Agents with Opik
OpenAI released an agentic framework aptly named Agents. What sets this framework apart from others is that it provides a rich set of core building blocks:
- Models: Support for all OpenAI Models
- Tools: Similar function calling functionality than the one available when using the OpenAI models directly
- Knowledge and Memory: Seamless integration with OpenAI’s vector store and Embeddings Anthropic
- Guardrails: Run Guardrails checks in parallel to your agent execution which allows for secure execution without slowing down the total agent execution.
Opik’s integration with Agents is just one line of code and allows you to analyse and debug the agent execution flow in our Open-Source platform.
Account Setup
Comet provides a hosted version of the Opik platform, simply create an account and grab your API Key.
You can also run the Opik platform locally, see the installation guide for more information.
Getting Started
Installation
First, ensure you have both opik and openai-agents packages installed:
Configuring Opik
Configure the Opik Python SDK for your deployment type. See the Python SDK Configuration guide for detailed instructions on:
- CLI configuration:
opik configure - Code configuration:
opik.configure() - Self-hosted vs Cloud vs Enterprise setup
- Configuration files and environment variables
Configuring OpenAI Agents
In order to use OpenAI Agents, you will need to configure your OpenAI API key. You can find or create your API keys in these pages:
You can set them as environment variables:
Or set them programmatically:
Enabling logging to Opik
To enable logging to Opik, simply add the following two lines of code to your existing OpenAI Agents code:
The Opik integration will automatically track both the token usage and overall cost of each LLM call that is being made. You can also view this information aggregated for the entire agent execution.
Example: Agents with Function Tools
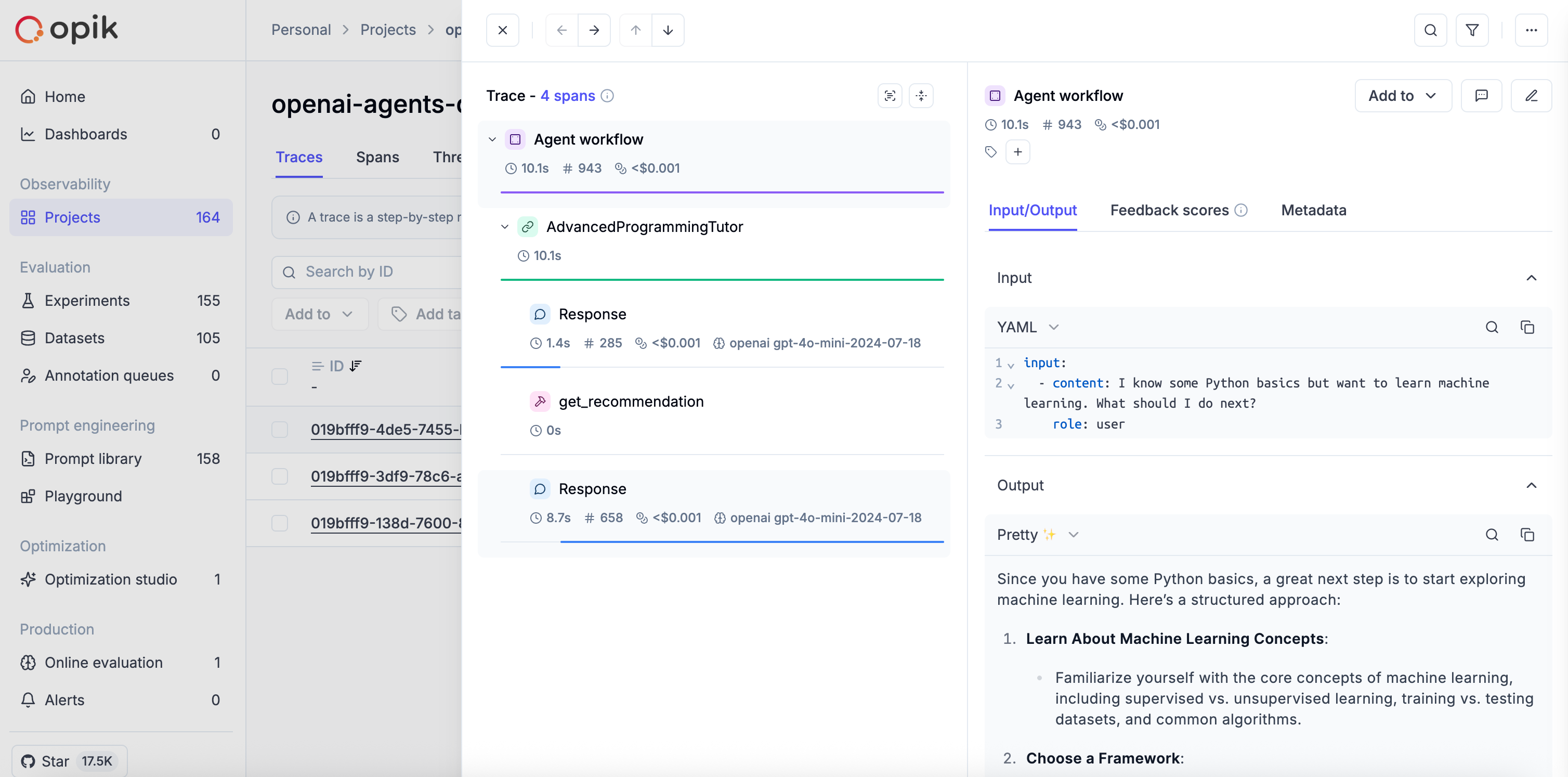
You can create agents with custom function tools. The OpikTracingProcessor automatically captures all tool calls as well:
Adding granularity with the @track decorator
If you need more visibility into what happens inside your tool functions, you can use the @track decorator to trace specific steps within the tool execution:
Logging threads
When you are running multi-turn conversations with OpenAI Agents using OpenAI Agents trace API, Opik integration automatically use the trace group_id as the Thread ID so you can easily review conversation inside Opik. Here is an example below:
Further improvements
OpenAI Agents is still a relatively new framework and we are working on a couple of improvements:
- Improved rendering of the inputs and outputs for the LLM calls as part of our
Pretty Modefunctionality - Improving the naming conventions for spans
- Adding the agent execution input and output at a trace level
If there are any additional improvements you would like us to make, feel free to open an issue on our GitHub repository.

