Observability for Harbor with Opik
Harbor is a benchmark evaluation framework for autonomous LLM agents. It provides standardized infrastructure for running agents against benchmarks like SWE-bench, LiveCodeBench, Terminal-Bench, and others.
Harbor enables you to evaluate LLM agents on complex coding tasks, tracking their trajectories using the ATIF (Agent Trajectory Interchange Format) specification.
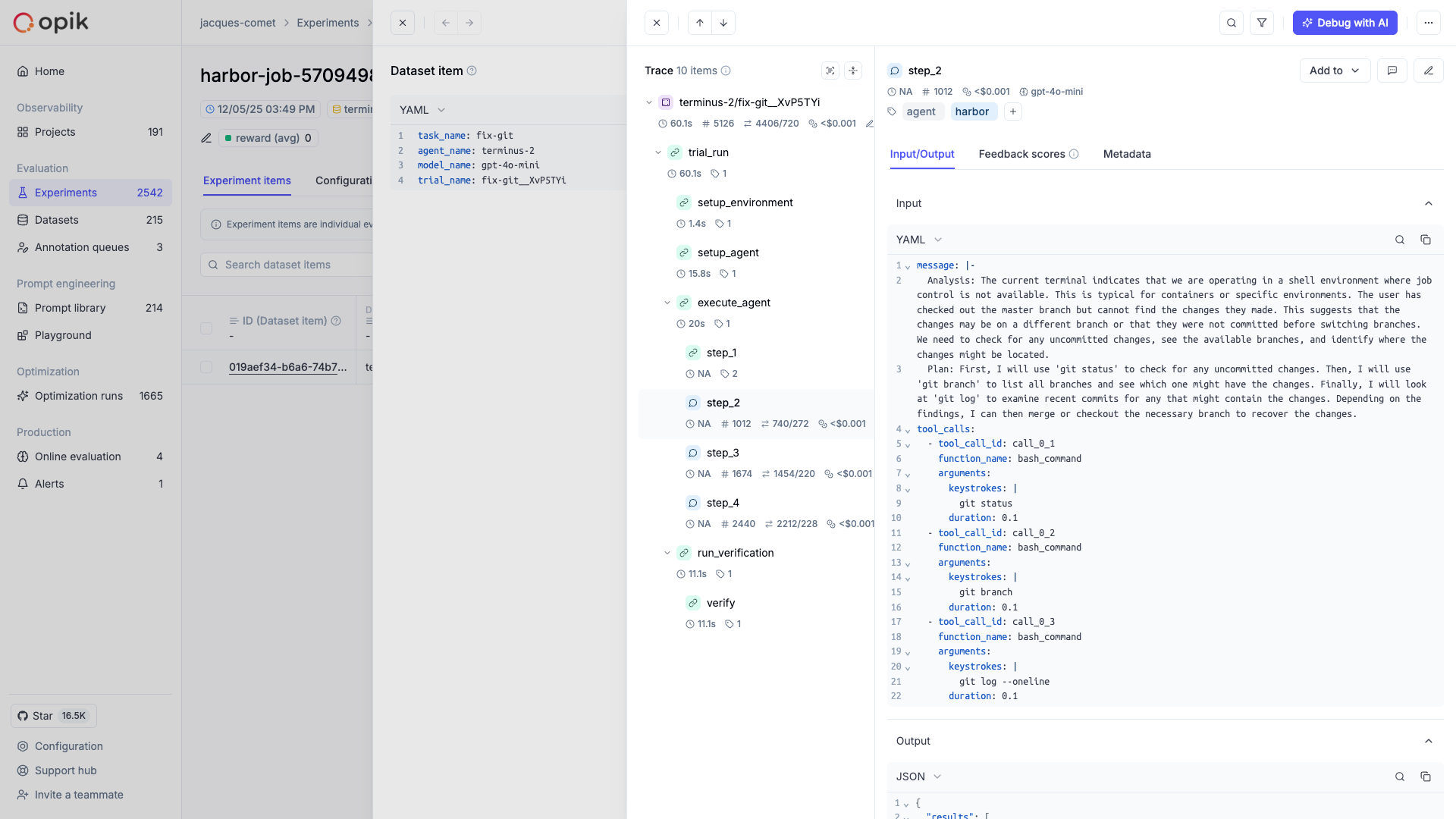
Opik integrates with Harbor to log traces for all trial executions, including:
- Trial results as Opik traces with timing, metadata, and feedback scores from verifier rewards
- Trajectory steps as nested spans showing the complete agent-environment interaction
- Tool calls and observations as detailed execution records
- Token usage and costs aggregated from ATIF metrics
Account Setup
Comet provides a hosted version of the Opik platform, simply create an account and grab your API Key.
You can also run the Opik platform locally, see the installation guide for more information.
Getting Started
Installation
First, ensure you have both opik and harbor installed:
Configuring Opik
Configure the Opik Python SDK for your deployment type. See the Python SDK Configuration guide for detailed instructions on:
- CLI configuration:
opik configure - Code configuration:
opik.configure() - Self-hosted vs Cloud vs Enterprise setup
- Configuration files and environment variables
Configuring Harbor
Harbor requires configuration for the agent and benchmark you want to evaluate. Refer to the Harbor documentation for details on setting up your job configuration.
Using the CLI
The easiest way to use Harbor with Opik is through the opik harbor CLI command. This automatically enables Opik tracking for all trial executions without modifying your code.
Basic Usage
Specifying Project Name
Available CLI Commands
All Harbor CLI commands are available as subcommands:
CLI Help
Example: SWE-bench Evaluation
Here’s a complete example running a SWE-bench evaluation with Opik tracking:
Custom Agents
Harbor supports integrating your own custom agents without modifying the Harbor source code. There are two types of agents you can create:
- External agents - Interface with the environment through the
BaseEnvironmentinterface, typically by executing bash commands - Installed agents - Installed directly into the container environment and executed in headless mode
For details on implementing custom agents, see the Harbor Agents documentation.
Running Custom Agents with Opik
To run a custom agent with Opik tracking, use the --agent-import-path flag:
Tracking Custom Agent Functions
When building custom agents, you can use Opik’s @track decorator on methods within your agent implementation. These decorated functions will automatically be captured as spans within the trial trace, giving you detailed visibility into your agent’s internal logic:
This allows you to trace not just the ATIF trajectory steps, but also the internal decision-making processes of your custom agent.
What Gets Logged
Each trial completion creates an Opik trace with:
- Trial name and task information as the trace name and input
- Agent execution timing as start/end times
- Verifier rewards (e.g., pass/fail, tests passed) as feedback scores
- Agent and model metadata
- Exception information if the trial failed
Trajectory Spans
The integration automatically creates spans for each step in the agent’s trajectory, giving you detailed visibility into the agent-environment interaction. Each trajectory step becomes a span showing:
- The step source (user, agent, or system)
- The message content
- Tool calls and their arguments
- Observation results from the environment
- Token usage and cost per step
- Model name for agent steps
Verifier Rewards as Feedback Scores
Harbor’s verifier produces rewards like {"pass": 1, "tests_passed": 5}. These are automatically converted to Opik feedback scores, allowing you to:
- Filter traces by pass/fail status
- Aggregate metrics across experiments
- Compare agent performance across benchmarks
Cost Tracking
The Harbor integration automatically extracts token usage and cost from ATIF trajectory metrics. If your agent records prompt_tokens, completion_tokens, and cost_usd in step metrics, these are captured in Opik spans.
Environment Variables
Getting Help
- Check the Harbor documentation for agent and benchmark setup
- Review the ATIF specification for trajectory format details
- Open an issue on GitHub for Opik integration questions

