Optimization Studio
Optimization Studio helps you improve prompts without writing code. You bring a prompt, define what “good” looks like, and Opik tests variations to find a better version you can ship with confidence. Teams like it because it shortens the loop from idea to evidence: you see scores and examples, not just a hunch. If you prefer a programmatic workflow, use the Optimize prompts guide.
Start an optimization
An optimization run is a structured way to improve a prompt. Opik takes your current prompt, tries small variations, and scores each one so you can pick the best-performing version with evidence instead of guesswork.
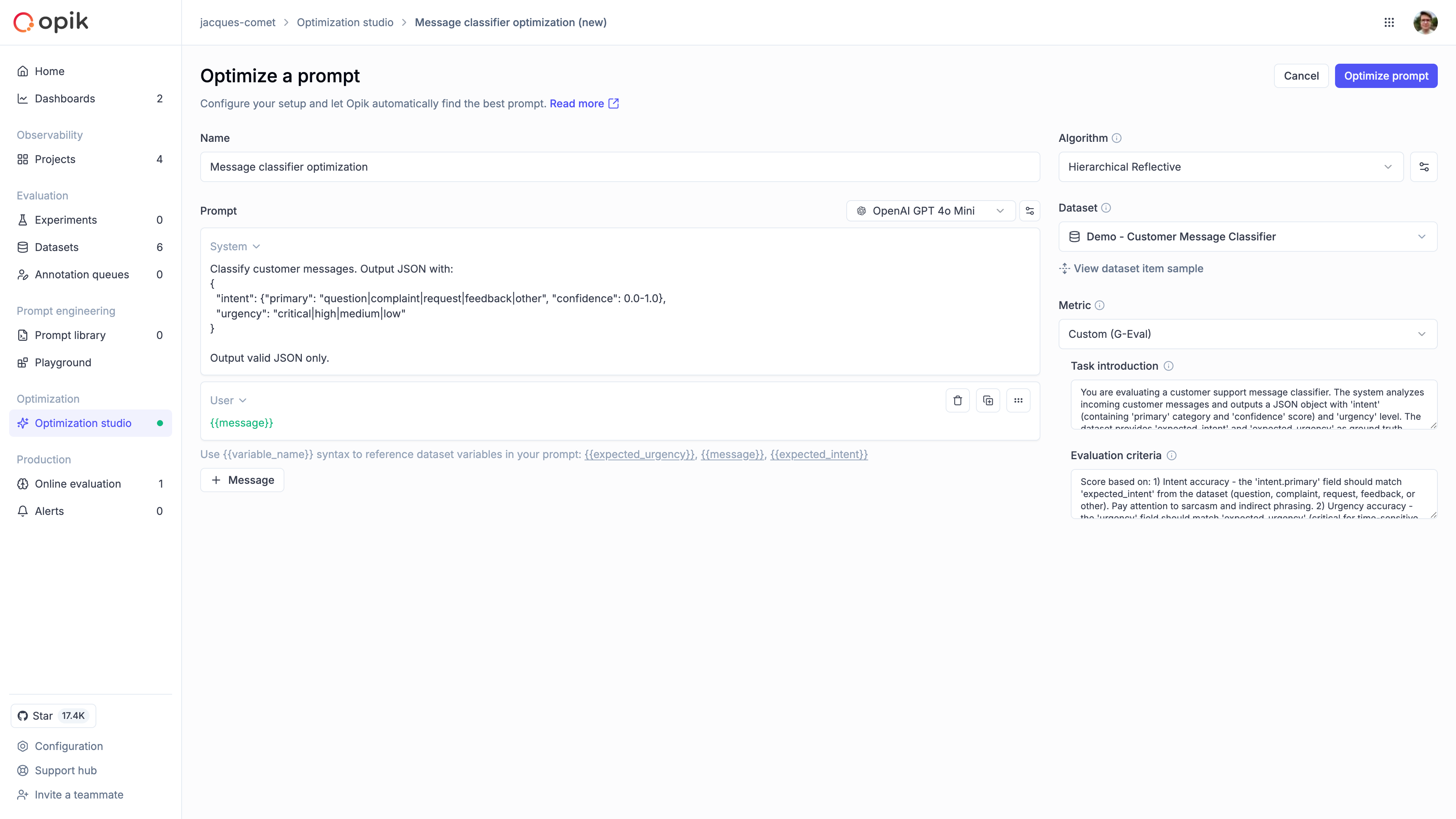
Configure the run
Name the run
Give the run a descriptive name so you can find it later. A good pattern is goal + dataset + date, for example “Support intent v1 - Jan 2026”.
Configure the prompt
Choose the model that will generate responses, then set the message roles (System, User, and so on). If your dataset has fields like question or answer, insert them with {{variable}} placeholders so each example flows into the prompt correctly. Start with the prompt you already use in production so improvements are easy to compare.
Pick an algorithm
Choose how Opik should search for better prompts. GEPA works well for single-turn prompts and quick improvements, while HRPO is better when you need deeper analysis of why a prompt fails. If you are new, start with GEPA to get a quick baseline, then switch to HRPO if you need deeper insight. For technical details, see Optimization algorithms.
Choose a dataset
Pick an existing dataset to supply examples. Aim for diverse, real-world cases rather than edge cases only, and keep the first run small so you can iterate quickly. If you need to create or upload data first, see Manage datasets.
Define a metric
Pick how Opik should score each prompt. Use Equals if the output should match exactly, or G-Eval if you want a model to grade quality. When using G-Eval, make sure the grading prompt reflects what “good” means for your task.
- Equals: Use when you have a single correct answer and want a strict match.
- G-Eval: Use when answers can vary and you want a model to score quality.
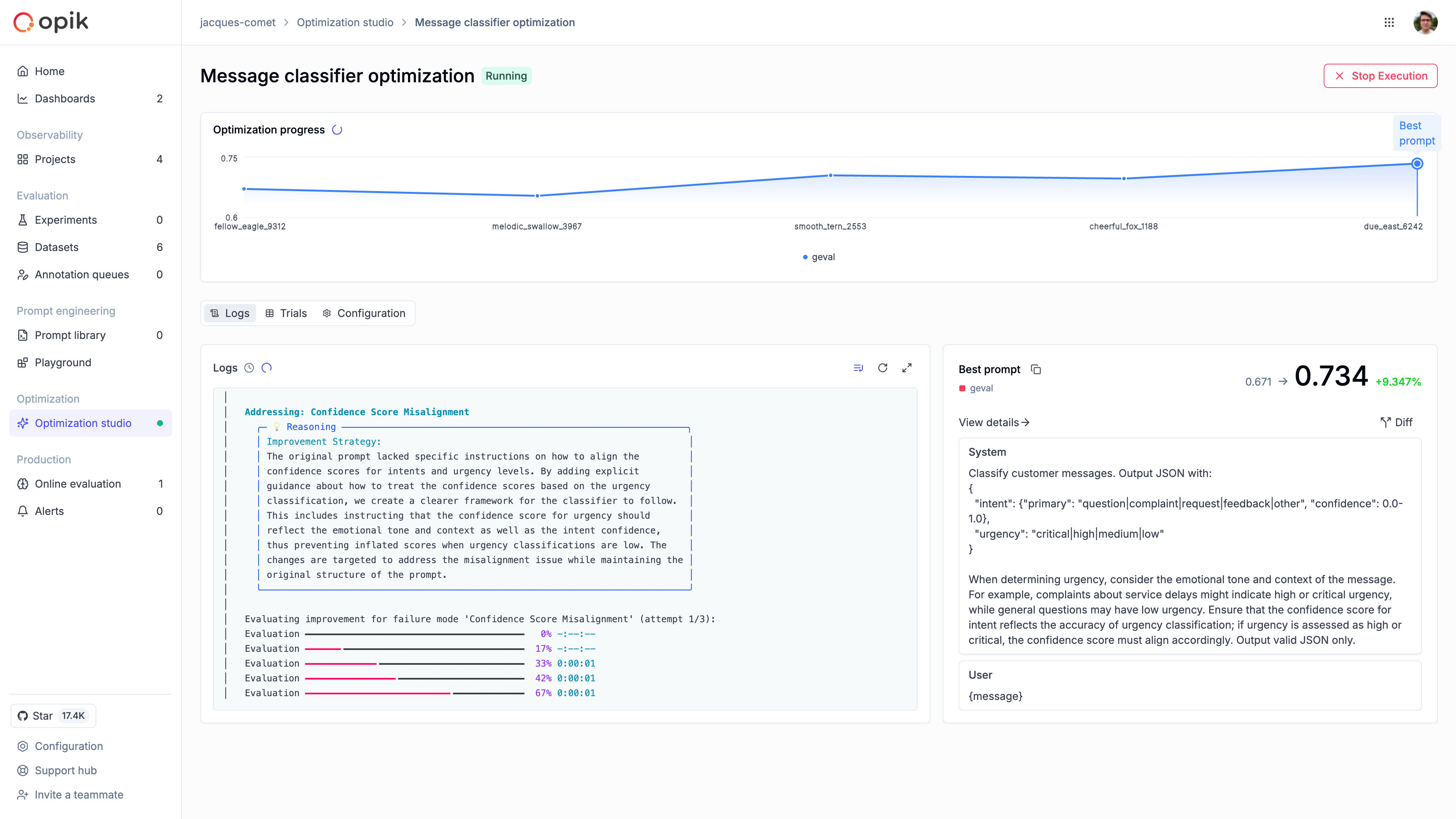
Monitor progress
Once the run starts, Optimization Studio shows the best score so far and a progress chart for each trial.
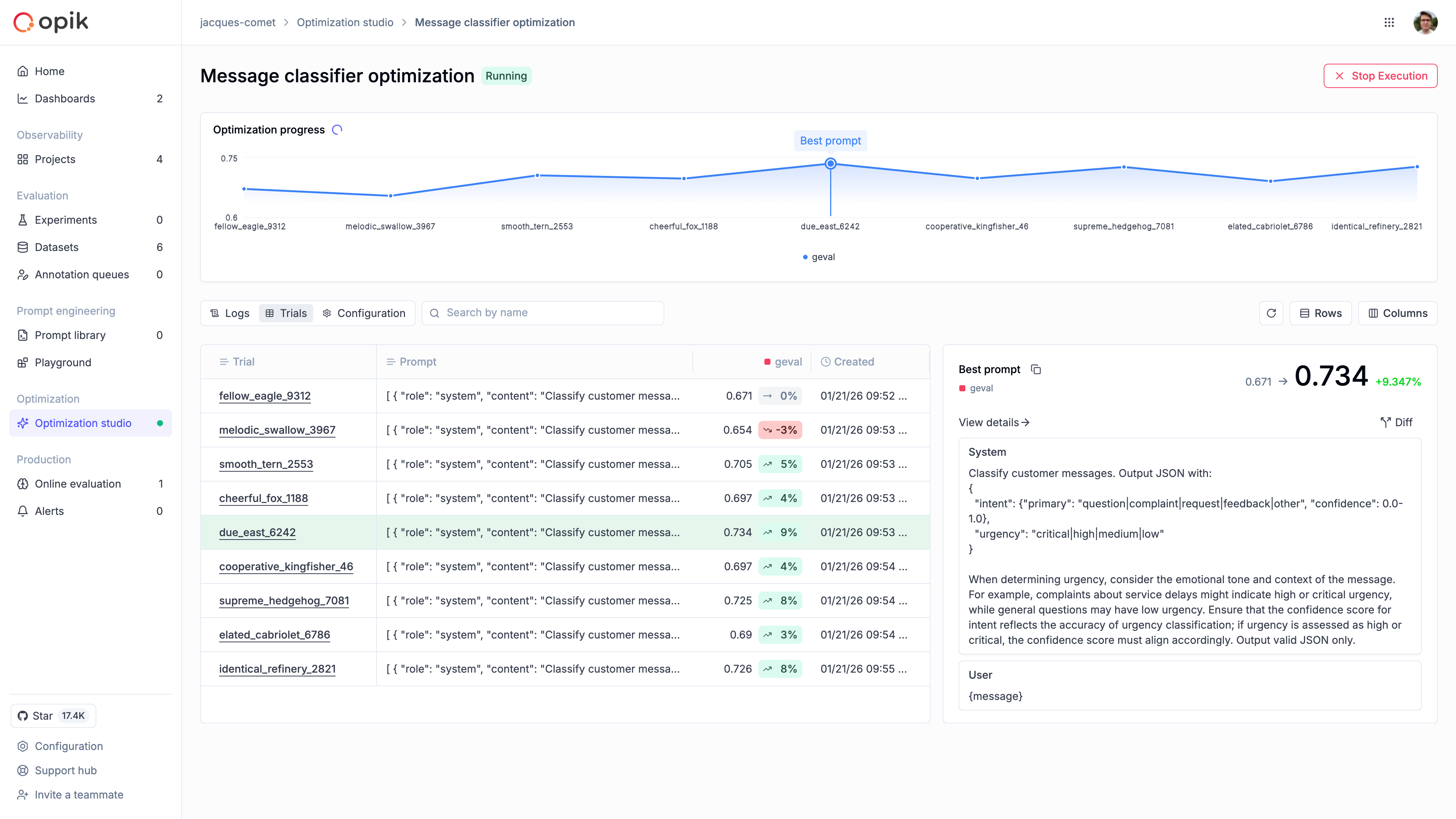
Analyze results
The Trials tab is where you compare prompt variations and scores, by clicking on a specific trial you can view the individual trial items that were evaluated.
Actions
You can rerun the same setup, cancel a run to change inputs, or select multiple runs to compare outcomes.
Reuse results outside the UI
If you want to automate optimizations in code later, follow Optimize prompts and use the same dataset and metric from this run.
Next steps
For a deeper breakdown of trials and traces, visit Dashboard results. If you want to automate this workflow, use Optimize prompts. To fine-tune your strategy, explore Optimization algorithms.

