Evolutionary Optimizer: Genetic Algorithms
Discover optimal prompts with genetic algorithms and multi-objective optimization.
The EvolutionaryOptimizer uses genetic algorithms to refine and discover effective prompts. It
iteratively evolves a population of prompts, applying selection, crossover, and mutation operations
to find prompts that maximize a given evaluation metric. This optimizer can also perform
multi-objective optimization (e.g., maximizing score while minimizing prompt length) and leverage
LLMs for more sophisticated genetic operations.
EvolutionaryOptimizer is a great choice when you want to explore a very diverse range of prompt
structures or when you have multiple objectives to optimize for (e.g., performance score and
prompt length). Its strength lies in its ability to escape local optima and discover novel prompt
solutions through its evolutionary mechanisms, especially when enhanced with LLM-driven genetic
operators.
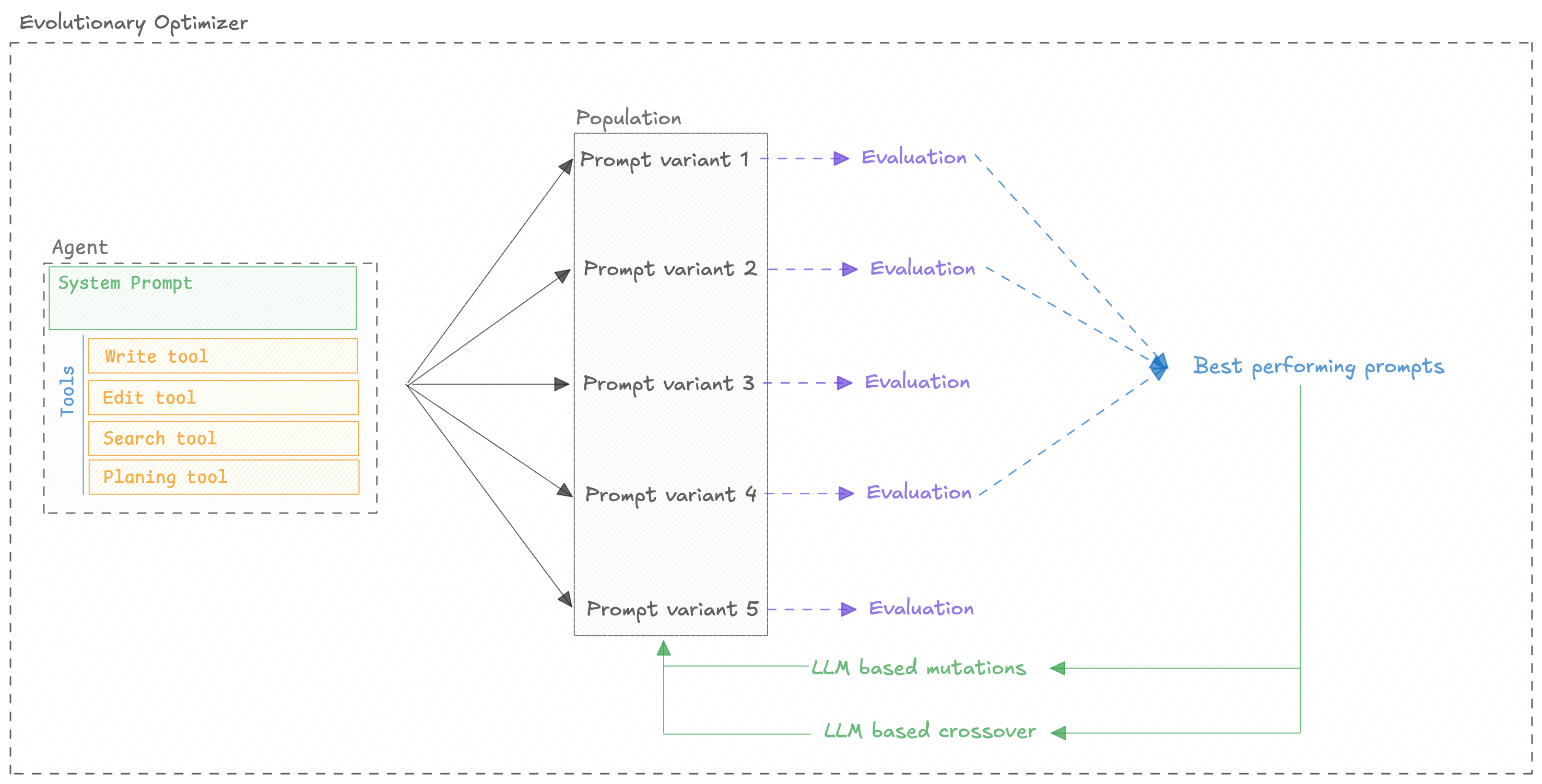
How It Works
The EvolutionaryOptimizer is built upon the DEAP library for
evolutionary computation. The core concept behind the optimizer is that we evolve a population of
prompts over multiple generations to find the best one.
We utilize different techniques to evolve the population of prompts:
- Selection: We select the best prompts from the population to be the parents of the next generation.
- Crossover: We crossover the parents to create the children of the next generation.
- Mutation: We mutate the children to create the new population of prompts.
We repeat this process for a number of generations until we find the best prompt.
The optimizer is open-source, you can check out the code in the Opik repository.
Quickstart
You can use the EvolutionaryOptimizer to optimize a prompt:
Configuration Options
Optimizer parameters
The optimizer has the following parameters:
optimize_prompt parameters
The optimize_prompt method has the following parameters:
dataset_item and llm_output50), fractions (e.g., 0.1), percentages (e.g., “10%”), or “all”/“full”/None for the full dataset.Model Support
There are two models to consider when using the EvolutionaryOptimizer:
EvolutionaryOptimizer.model: The model used for the evolution of the population of prompts.ChatPrompt.model: The model used to evaluate the prompt.
The model parameter accepts any LiteLLM-supported model string (e.g., "gpt-4o", "azure/gpt-4",
"anthropic/claude-3-opus", "gemini/gemini-1.5-pro"). You can also pass in extra model parameters
using the model_parameters parameter:
Next Steps
- Explore specific Optimizers for algorithm details.
- Refer to the FAQ for common questions and troubleshooting.
- Refer to the API Reference for detailed configuration options.

