MetaPrompt Optimizer
The MetaPrompter is a specialized optimizer designed for meta-prompt optimization. It focuses on improving the structure and effectiveness of prompts through systematic analysis and refinement of prompt templates, instructions, and examples.
The MetaPromptOptimizer is a strong choice when you have an initial instruction prompt and want to
iteratively refine its wording, structure, and clarity using LLM-driven suggestions. It excels at
general-purpose prompt improvement where the core idea of your prompt is sound but could be
phrased better for the LLM, or when you want to explore variations suggested by a reasoning model.
How it works
The MetaPromptOptimizer automates the process of prompt refinement by using a “reasoning” LLM to
critique and improve your initial prompt. Here’s a conceptual breakdown:
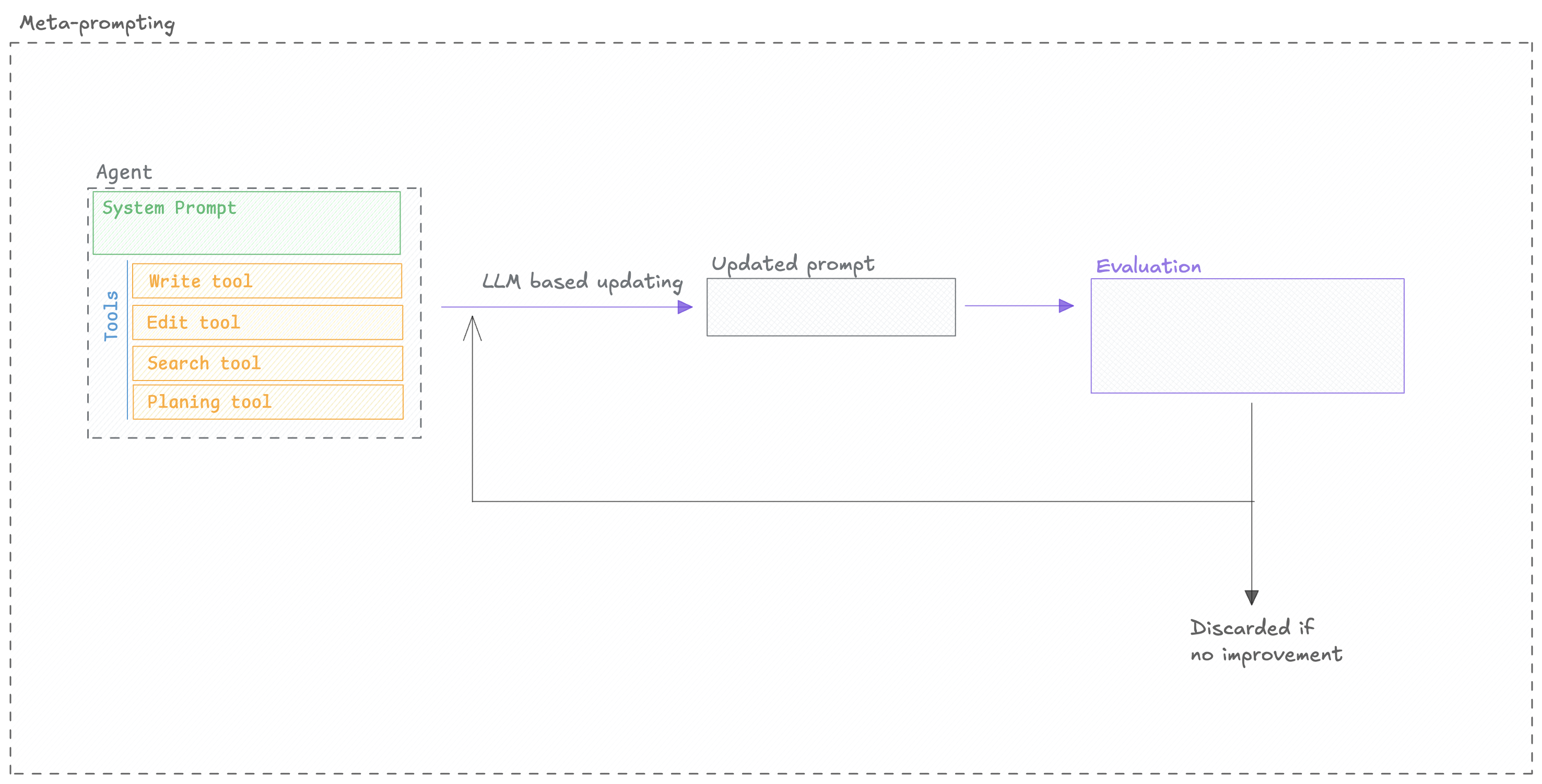
The optimizer is open-source, you can check out the code in the Opik repository.
Quickstart
You can use the MetaPromptOptimizer to optimize a prompt by following these steps:
Configuration Options
Optimizer parameters
The optimizer has the following parameters:
optimize_prompt parameters
The optimize_prompt method has the following parameters:
50), fractions (e.g., 0.1), percentages (e.g., “10%”), or “all”/“full”/None for the full dataset.Model Support
There are two models to consider when using the MetaPromptOptimizer:
MetaPromptOptimizer.model: The model used for the reasoning and candidate generation.ChatPrompt.model: The model used to evaluate the prompt.
The model parameter accepts any LiteLLM-supported model string (e.g., "gpt-4o", "azure/gpt-4",
"anthropic/claude-3-opus", "gemini/gemini-1.5-pro"). You can also pass in extra model parameters
using the model_parameters parameter:
MCP Tool Calling Support
The MetaPrompt Optimizer is the only optimizer that currently supports MCP (Model Context Protocol) tool calling optimization. This means you can optimize prompts that include MCP tools and function calls.
MCP tool calling optimization is a specialized feature that allows the optimizer to understand and optimize prompts that use external tools and functions through the Model Context Protocol. This is particularly useful for complex agent workflows that require tool usage.
For comprehensive information about tool optimization, see the Tool Optimization Guide.

