GEPA Optimizer
Single-turn system prompt optimization with reflection
GepaOptimizer wraps the external GEPA package to optimize a
single system prompt for single-turn tasks. It maps Opik datasets and metrics into GEPA’s expected
format, runs GEPA’s optimization using a task model and a reflection model, and returns a standard
OptimizationResult compatible with the Opik SDK.
GepaOptimizer is ideal when you have a single-turn task (one user input → one model
response) and you want to optimize the system prompt using a reflection-driven search.
How it works
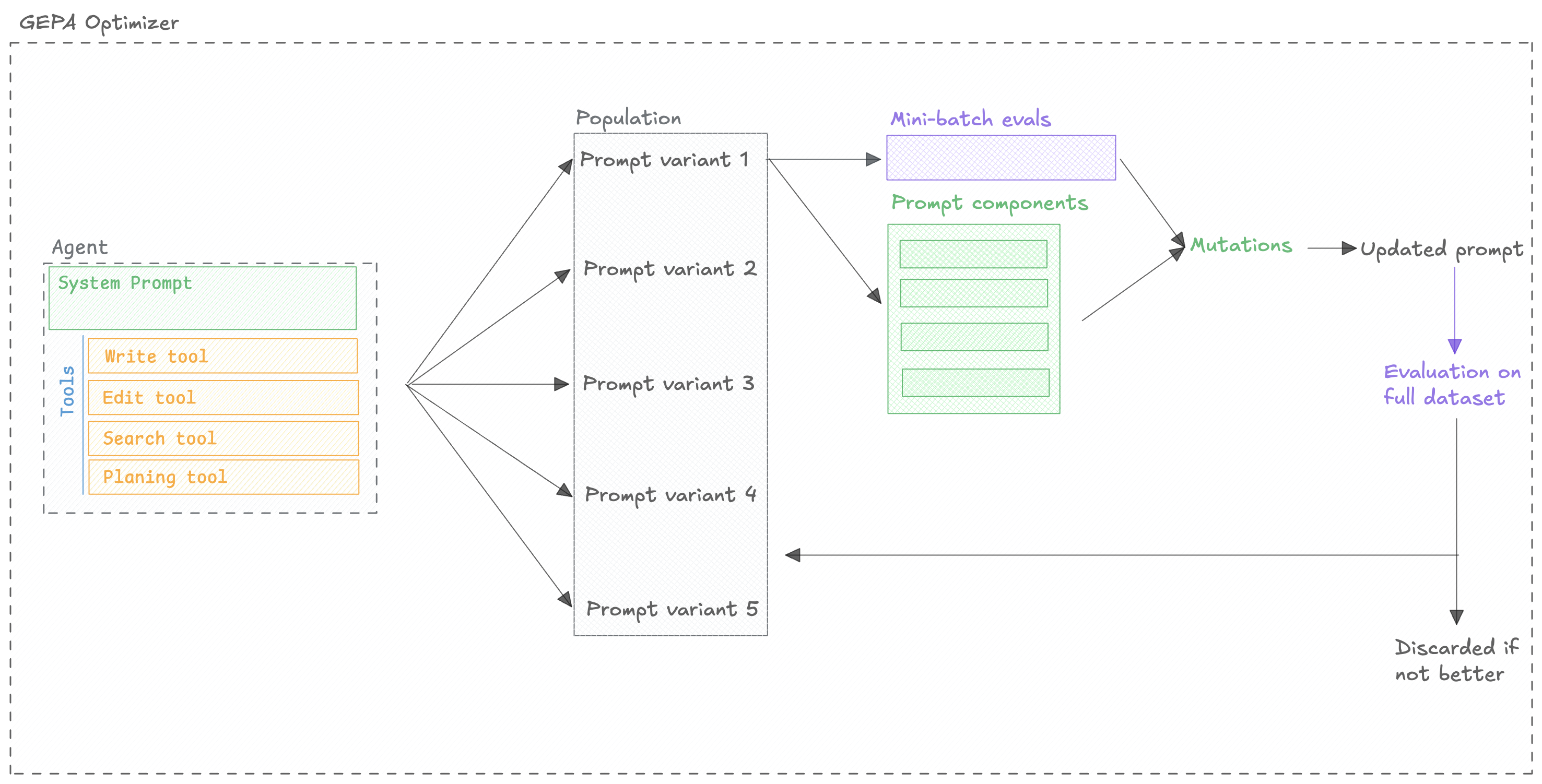
The GEPA optimizer companies two key approaches to optimize agents:
- Reflection: The optimizer uses the outcomes from evaluations to improve the prompts.
- Evolution: The optimizer uses an evolutionary algorithm to explore the space of prompts.
You can learn more about the algorithm in the GEPA paper but in short, the optimizer will:
Quickstart
Determinism and tool usage
- GEPA’s seed is forwarded directly to the underlying
gepa.optimizecall, but any non-determinism in your prompt (tool calls, non-zero temperature, external APIs) will still introduce variance. To test seeding in isolation, disable tools or substitute cached responses. - GEPA emits its own baseline evaluation inside the optimization loop. You’ll see one baseline score from Opik’s wrapper and another from GEPA before the first trial; this is expected and does not double-charge the metric budget.
- Reflection only triggers after GEPA accepts at least
reflection_minibatch_sizeunique prompts. If the minibatch is larger than the trial budget, the optimizer logs a warning and skips reflection.
GEPA scores vs. Opik scores
- The GEPA Score column reflects the aggregate score GEPA computes on its train/validation split when deciding which candidates stay on the Pareto front. It is useful for understanding how GEPA’s evolutionary search ranks prompts.
- The Opik Score column is a fresh evaluation performed through Opik’s metric pipeline on the same dataset (respecting
n_samples). This is the score you should use when comparing against your baseline or other optimizers. - Because the GEPA score is based on GEPA’s internal aggregation, it can diverge from the Opik score for the same prompt. This is expected—treat the GEPA score as a hint about why GEPA kept or discarded a candidate, and rely on the Opik score for final comparisons.
skip_perfect_score
- When
skip_perfect_score=True, GEPA immediately ignores any candidate whose GEPA score meets or exceeds theperfect_scorethreshold (default1.0). This keeps the search moving toward imperfect prompts instead of spending budget refining already perfect ones. - Set
skip_perfect_score=Falseif your metric tops out below1.0, or if you still want to see how GEPA mutates a perfect-scoring prompt—for example, when you care about ties being broken by Opik’s rescoring step rather than GEPA’s aggregate.
Configuration Options
Optimizer parameters
The optimizer has the following parameters:
optimize_prompt parameters
The optimize_prompt method has the following parameters:
50), fractions (e.g., 0.1), percentages (e.g., “10%”), or “all”/“full”/None for the full dataset.Model Support
GEPA coordinates two model contexts:
GepaOptimizer.model: LiteLLM model string the optimizer uses for internal reasoning (reflection, mutation prompts, etc.).ChatPrompt.model: The model evaluated against your dataset—this should match what you run in production.
Set model to any LiteLLM-supported provider (e.g., "gpt-4o", "azure/gpt-4", "anthropic/claude-3-opus", "gemini/gemini-1.5-pro") and pass extra parameters via model_parameters when you need to tune temperature, max tokens, or other limits:
Reflection is handled internally; there is no separate reflection_model argument to set.
Limitations & tips
- Instruction-focused: The current wrapper optimizes the instruction/system portion of your prompt. If you rely heavily on few-shot exemplars, consider pairing GEPA with the Few-Shot Bayesian optimizer or an Evolutionary run.
- Reflection can misfire: GEPA’s reflective mutations are only as good as the metric reasons you supply. If
ScoreResult.reasonis vague, the optimizer may reinforce bad behaviors. Invest in descriptive metrics before running GEPA at scale. - Cost-aware: Although GEPA is more sample-efficient than some RL-based methods, reflection and Pareto scoring still consume multiple LLM calls per trial. Start with small
max_trialsand monitor API usage.
Next Steps
- Explore specific Optimizers for algorithm details.
- Refer to the FAQ for common questions and troubleshooting.
- Refer to the API Reference for detailed configuration options.

